
If this number is high, the model is a good fit for your data. Named in honor of Sir Ronald Fisher, the F-test for the null hypothesis checks the overall validity of your model. The mean sum of squared residuals is a number calculated by dividing the sum of squares by the corresponding degrees of freedom ( SS/df.) It is also used to determine the spread of the data points. If the number is high, that indicates a huge variation in the data – which means that your model is not the most optimal way to analyze a given data set. The sum of squares helps measure the deviation of your data from the mean value.
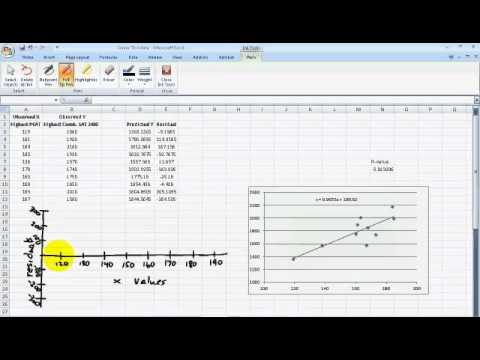
The results of the ANOVA test are presented in the ANOVA table.ĭ egrees of freedom is the number of logically independent values. It examines the differences between groups of data to identify whether they are caused by systematic (statistically significant) or random (statistically non-significant) factors. ANOVA TableĪnalysis of variance (ANOVA) determines the significance of your research. This value indicated the overall number of observations used in your regression model, plain and simple. The standard error of the regression shows the standard deviation of the coefficient by estimating the average distance between the observed values and the regression line.
Therefore, it is a perfect choice for multiple regression analysis with a lot of independent variables. This modified version of R² takes into consideration the number of predictors in a regression model. For example, our R² is ~0,895, so we can conclude that our regression model does a great job at showing the relationship between the data points. The closer the coefficient is to 1, the more robust and reliable the model is.
#Residual plot how to#
If you work with raw data, here’s how to square a number in Excel. It shows the relationship between the observed and predicted data values, which makes it a primary indicator of a good model. R SquareĬalled the coefficient of determination, this number is calculated as (Multiple R)².
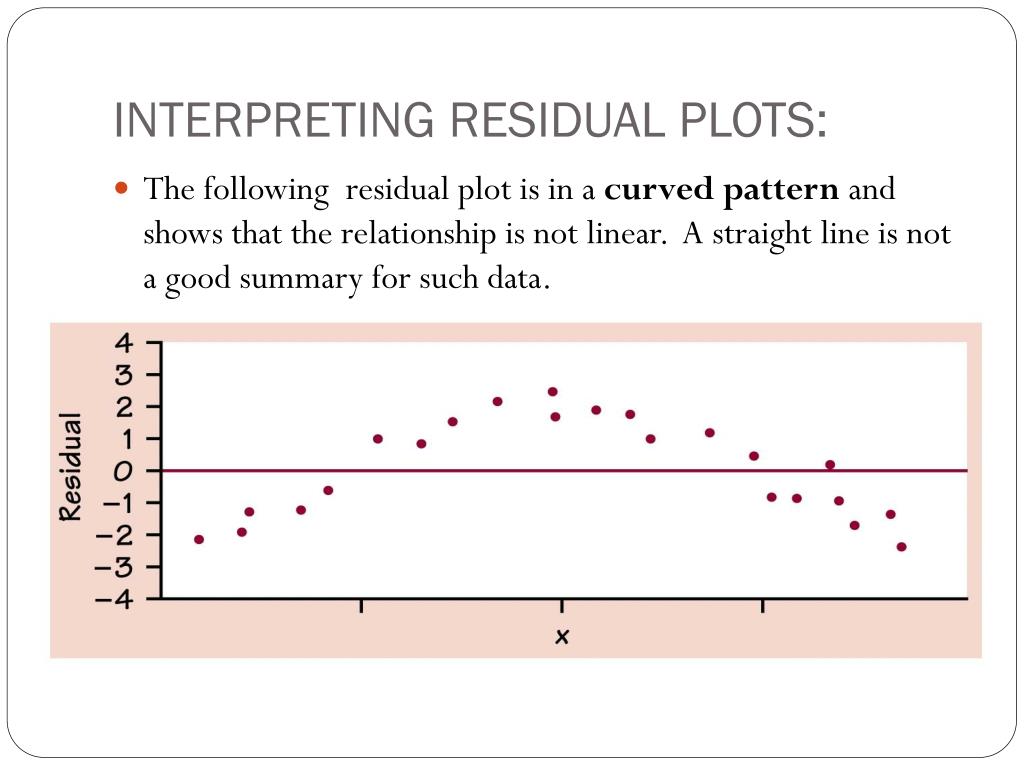
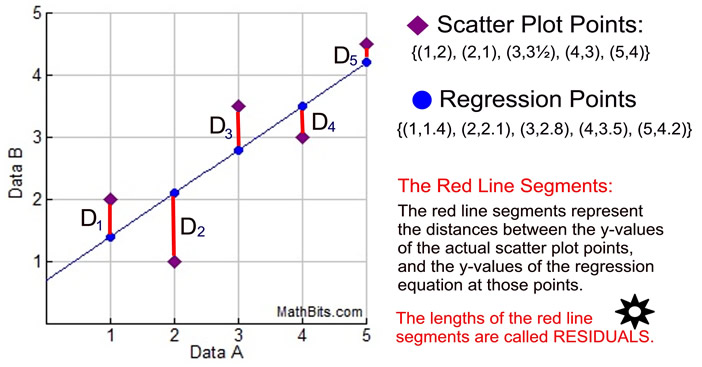
Long story short, if you don’t know whether a given regression model is suitable for your data, creating a residual plot is one of the quickest ways to test it out.



 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
